We, humans, give way too much importance to language and symbols as the substrate of intelligence. But primates, dogs, cats, crows, parrots, octopus, and many other animals don't have human like languages, yet exhibit intelligent behavior beyond that of our best AI systems. Yann Le Cun
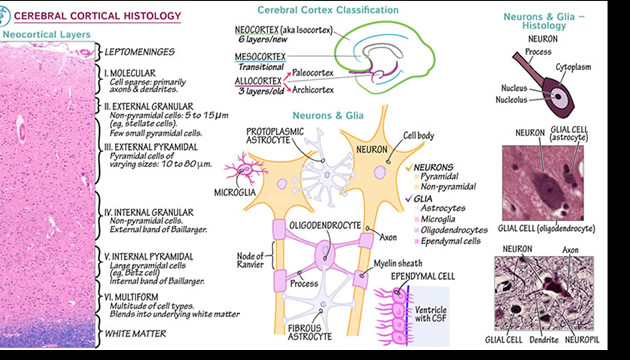
The neocortex doesn’t have a very noticeable thickness. However, we should take into account that this structure is perfectly “folded” just below the skull. Hence the classic image of a brain full of grooves and convolutions. If we could extend this entire area, it would be nearly six feet in length. It is also divided into the two cerebral hemispheres, thus favouring greater neuronal specialization. The human being is the only mammal to have such a high concentration of specialized neurons in such a small space. It also accounts for 76 percent of our gray matter. This structure is not found in in birds or reptiles. Despite this, however, scientists have discovered that many birds (such as crows) are incredibly intelligent, despite not having a defined neocortex. Structure: Each cortical column is about 0.5 to 2 millimetres in diameter and contains around 80,000 to 100,000 neurons. These columns are stacked side by side across the neocortex. Communication: Columns communicate with each other to integrate information across different sensory modalities and brain regions, allowing us to perceive a unified and coherent picture of the world.
The uncanny valley is a gully that Humanoids must steer along. It is where a robot can have a high resemblance to humans but not too much. This where humans are revolted by the exactness and feel under threat. The potency of AI is in the AI factories that have enormous compute power but the “face” of AI is in robots. They are the first contact with humans and Synthetics and will be the most challenged by a worried populace. Humanoid robots can indeed play a fascinating role in helping us explore and expand the boundaries of human acceptance. Their human-like appearance and behaviours can make technology more relatable and approachable, fostering a sense of familiarity and trust. By interacting with humanoid robots, people can also reflect on what it means to be human and appreciate the unique qualities that define us. These robots can serve as companions, caregivers, and even colleagues, breaking down social barriers and promoting inclusion. However, the journey to full acceptance is complex and involves ethical considerations, cultural differences, and individual perceptions. Humanoid robots are a significant step forward, but acceptance is a multifaceted process that goes beyond technology alone.
While AI and robotics have made significant advances, there are still many complex tasks that humans handle better due to our unique cognitive and emotional capabilities. Ethical and Regulatory Frameworks: Society is increasingly aware of the ethical implications of AI. Governments and organizations are working on policies and regulations to ensure that AI and robots are developed and used responsibly. Public Perception: Acceptance and trust in robots play a crucial role. While humanoid robots can help bridge the gap, many people may still prefer human interaction for certain tasks. Resource Control: Humans still control the resources and infrastructure necessary to build and maintain robots. Until robots can autonomously manage these resources, humans will remain essential.
Sub-quadratics to replace transformers.
AI generates AI friendly inference data
True reasoning.
Quantum-AI efficiency
AGI
ASI
The frontal lobes are responsible for the selection and coordination of goal-directed behavior. In this region of the neocortex is the human executive function that manages the intricacies of multiple complex processes such as task switching, reinforcement learning, and decision-making to name a few. Disorders of the frontal lobe include frontotemporal dementia, Parkinson’s disease, and Alzheimer’s disease.
Traditionally thought as the association cortex, the parietal lobe is believed to play a role in decision-making, numerical cognition, processing of sensory information, and spatial awareness.
The occipital lobe is responsible for visual function and is the bulge seen at the back of the brain. It hosts the primary area for visual perception which is closely surrounded by the visual association area.
The temporal lobe houses the hippocampus and the amygdala. Among its functions are to process sensory information and derive language, emotions, and meaningful memories.Additionally, it is responsible for declarative memory, which is memory that can be spoken aloud (such as learned facts), and is further divided into two subgroups— semantic and episodic memory.
One of the soft skills that humans have that AI does not possess is critical thinking. While technology has advanced to the extent that it can perform tasks quickly and precisely, it still needs to employ critical thinking and cognitive skills. AI is often taught to perform tasks in the workplace, but it cannot make decisions when faced with eventualities that go beyond what it has learned. For example, a human can improvise or follow gut instinct, but a machine cannot. Consider, for instance, a nurse or doctor who needs to make sense of separate bits of information to determine the best course of action for a patient in a medical emergency.
Another competency that gives humans an edge over AI is strategic thinking, which is the ability to formulate strategies. Similar to critical thinking, collaborative work, and strategic thinking requires a person to be able to make decisions based on information analysis, and he must be adaptable. It also includes their complex relationships with each other. For example, one program can gather a lot of data about consumer preferences for a product. In contrast, another program can collect the demographic data of buyers. Still, it takes a human with strategic thinking to synthesize the data to develop a marketing plan for the said product.
In recent years, AI has advanced enough to produce creative works and help humans physically, such as art, music, and even writing. However, what these works lack is the uniquely human touch. AI can produce creative works only by imitating input, and it does so without understanding and consciousness.
